Anti-inflammatory
See also : inflammatory diseases
Contents
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Research suggests that people with a high intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, healthy oils and fish may have a reduced risk for inflammation-related diseases. In addition, substances found in some foods (especially antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids) appear to possess anti-inflammatory effects.
The anti-inflammatory diet is an eating plan designed to reduce chronic inflammation, a key factor in a host of health problems and several major diseases.
In chronic inflammation, the immune system continually releases chemicals that are typically responsible for combating harmful substances like viruses and bacteria. Often resulting from lifestyle factors like stress and lack of exercise, chronic inflammation occurs even when there are no foreign invaders to fight off.
Syndromes of inflammation
Since nutrition can also influence inflammation, the anti-inflammatory diet is thought to curb chronic inflammation and help prevent or treat the following conditions:
- allergies
- Alzheimer's disease
- asthma
- cancer
- diabetes
- heart disease
- inflammatory bowel disease (such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease)
- irritable bowel syndrome
- stroke
- Arthritis
- Rheumatism
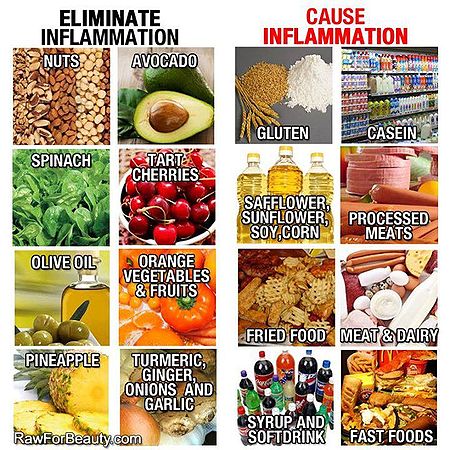
Foods to Include in the Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Research suggests that people with a high intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, seeds, healthy oils and fish may have a reduced risk for inflammation-related diseases. In addition, substances found in some foods (especially antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids) appear to possess anti-inflammatory effects.
- Foods high in antioxidants include: berries, cherries, apples, artichokes, dark green leafy vegetables (such as kale, spinach, and collard greens), sweet potatoes, broccoli, nuts (such as pistachios, almonds, and pecans), beans, whole grains (especially oats), dark chocolate.
- Vitamin D : One of the easiest and most powerful ways to prevent inflammation-related disease, vitamin D, which is naturally produced in the body as a result of exposure to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation, is crucial for quelling chronic inflammation.
- ginger may reduce inflammation more effectively than non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as aspirin).
- Curcumin (turmeric). There are easily hundreds of published studies that demonstrate turmeric's amazing anti-inflammatory benefits. What distinguishes curcumin is its ability to reduce inflammation through at least ninety-seven different biological mechanisms. Studies found that turmeric’s anti-inflammatory effects are on a par with potent drugs such as hydrocortisone and Motrin, but yet having none of their side effects.
- Modified Citrus Pectin : The wide-ranging success of this MCP against both acute and chronic inflammatory conditions, is largely derived from its unique relationship with the causative biomarker molecule, galectin-3 (Gal-3).
- Acai berries contain anti-inflammatory properties.
- Kelp such as kombu contains fucoidan, a type of complex carbohydrate that is anti-inflammatory.
- Cloves contain an anti-inflammatory chemical called eugenol.
- Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids include: oily fish (such as salmon, herring, mackerel, sardines and tuna), flaxseed, walnuts, omega-3-fortified foods (including eggs and milk)
- Copaiba has greater action than Ibuprofen or even Cortisone -Copaiba decreases PGE2 production, and it is a Cox-2 inhibitor – making it very good for heart health (similar to why you would take an aspirin a day).
- Acacia : The antioxidant activity is believed to be responsible for the anti-inflammatory activity.
- Flavonoids increase neurogenesis in the hippocampus of stressed rats, possibly by increasing blood flow to the brain and/or increasing levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).BDNF is a remarkable rejuvenator in several respects. In your brain, BDNF not only preserves existing brain cells, it also activates brain stem cells to convert into new neurons and effectively makes your brain grow larger.
- Salmon is an excellent source of EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), two potent omega-3 fatty acids that douse inflammation. The benefits of omega-3 have been backed by numerous studies and they range from preventing heart disease and some cancers to reducing symptoms of autoimmune diseases and psychological disorders.
- shiitake: Enjoyed by the Chinese and the Japanese since ancient times, shiitake mushroom is revered for its immune-boosting properties and its mild smoky taste.
- The flavonoids in Green Tea are potent natural anti-inflammatory compounds that have been shown in numerous studies to reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer.
- papaya contains papain, a protein-digesting enzyme. Together with other nutrients such as vitamin C and E, papain helps to reduce inflammation, and improves digestion and healing from burns.
- Bromelain is an anti-inflammatory enzyme.
- Beta glucan : In a study conducted at the University UFRN located in Brazil, researchers concluded that the glucan has anti-inflammatory properties that are a result of the inhibition of both nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and cyclooxygenase (COX)
- Cherries contain anthocyanins working like a natural form of ibuprofen, reducing inflammation and curbing pain.
- Blueberry, Raspberry, Blackberry, and Strawberries have similar anti-inflammatory effects as cherries.
- The monounsaturated fats in Olive Oil are turned into anti-inflammatory agents by the body that can lower occurrences of asthma and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Flaxseeds are high in natural oils that convert into hormone-like substances in the body to reduce inflammatory substances.
- Walnuts: Like flax seeds, raw, unsalted walnuts contain plentiful amounts of Omega 3 fatty acids that decrease pain and inflammation.
- Broccoli is a highly nutritious vegetable that contains anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer phytonutrients such as sulforaphane which helps the body to get rid of potentially carcinogenic compounds.
- Sweet Potato is also a good source of complex carbohydrate, beta-carotene, manganese, vitamin B6 and C as well as dietary fiber. Working in concert, these nutrients are powerful antioxidants that help to heal inflammation in the body.
- saponin : Saponins have hemolytic, expectorative, anti-inflammatory and immune-stimulating activity. Beyond that, saponins demonstrate antimicrobial properties particularly against fungi and additionally against bacteria and protozoa.
- Quercetin acts as an anti-inflammatory
- The resin secreted by the guggul tree are found to have anti-inflammatory and cholesterol-lowering effects.
- Holy Basil oil is found to possess anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and other medicinal properties that are effective against arthritis, diabetes, high cholesterol, peptic ulcers as well as chemotherapy and radiation poisoning.
- Rosemary : Rosmarinic acid increases the production of prostaglandin E2 (substances that help in contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle, the dilation and constriction of blood vessels, control of blood pressure, and modulation of inflammation) and reduces the production of leukotriene B4 involved in inflammation.
- Neem oil is used in Ayurvedic medicine to calm inflammatory skin conditions, joint pains and muscle aches. Extracts of neem leaves and seeds have also demonstrated anti-fungal, antibacterial, anti-diabetic and anti-viral properties in various studies.
- Aloe Vera‘s anti-inflammatory properties work internally as well. When ingested, aloe cools inflammation in the digestive tract such as in the case of peptic ulcers, and it may also be beneficial for other inflammatory conditions.
- the strong anti-inflammatory compounds found in licorice root have been found to be effective against coughs, colds, mouth ulcers, peptic ulcers and even chronic hepatitis infection.
- Saw palmetto shows promising anti-inflammatory activity against the enlargement of the prostate gland in men.
- feverfew : this anti-inflammatory herb can help to lower fever, and it’s also effective in reducing the severity and frequency of headaches and migraines.
- the bark of slippery elm has been used to address a wide range of health concerns, such as cough, sore throat, irritable bowel syndrome, gastritis, arthritis as well as other inflammatory conditions.
- Astaxanthin is a red pigment found in different strains of algae, phytoplankton and plants. The substance is known to be the most potent known antioxidant, it has a natural and scientifically proven anti-inflammatory ability.
- Ellagic Acid may be effective against inflammation.
- serrapeptase offers help for allergies, asthma, arthritis, MS, and other inflammatory diseases.
- Camu camu may fight inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Boswellia blox the enzyme enzyme called 5-lipoxygenase or 5-LOX responsable for inflammatory diseases like arthritis.
- Olives are rich in anti-inflammatory ingredients called hydroxytyrosol and oleocanthal. In 2005, a study conducted by Monell Chemical Senses Center found these two compounds to have anti-inflammatory effects.
- white tea, Witch Hazel and rose stops destructive inflammation, fights cancer and prevents aging.
- Chamomile also has anti-inflammatory properties.
- People who regularly practice yoga may have reduced levels of interleukin-6 (a marker of inflammation)
- Luo Han Guo exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties that may protect against liver and skin cancer.
- lemongrass leaves have been used traditionally to treat a variety of conditions including inflammation.
- Licorice : A substance in licorice has the capacity to stop the activation of two of the main enzymes that initiate inflammation - cyclooxygenase and lipooxygenase. Licorice also brings up the human body’s automatic anti-inflammatory response. That is the reason why several drugs to prevent the effects of arthritis are added with licorice, particularly black licorice.
- Ginseng is popular in Chinese medicine, and modern researches have discovered that this is due to the anti-inflammatory properties of ginseng. In a study made at the University of Hong Kong by a research team led by Allan Lau, ginseng contains ginsenosides, substances that can suppress the activities of the immune system. By this activity, inflammatory responses are inhibited. Although this finding brings hope for those suffering from various types of inflammatory diseases, using ginseng must always be consulted with the physician.
- Oregano : In a study of Kyoji Yoshino’s team at the Numazu College of Technology, they found out that oregano has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect through its phytonutrients, the rosmarinic acid and thymol. While its anti-inflammatory effects is weaker compared to hydrocortisone, the activities of the antioxidant properties of oregano can actually prevent disease caused by inflammation, which basically makes oregano an effective anti-inflammatory herb.
- Garlic due to diallyl sulphide and thiacremonone. 1,2-DT (1,2-vinyldithiin) is one of the unique sulfur compounds in garlic that has long been recognized as having anti-inflammatory properties.
- Onions are packed with anti-inflammatory agents.
- Cayenne Pepper : Whatever form chili peppers are, may it be cayenne pepper or bell pepper, they have been known to fight inflammation in the body. Just two teaspoons of powdered cayenne pepper can already deliver at least 30 percent of the daily requirement for vitamin A. In fewer calories, it also provides vitamins E, C, K and B6. Cayenne pepper contains capsaicin, which, according to researches, inhibits substance P. Neuropeptide, substance P, is linked with the process of inflammation.
- Yucca schidigera is a medicinal plant native to Mexico. According to folk medicine, yucca extracts have anti-arthritic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Asparagus is rich in anti-inflammatory properties.
- Quercetin has anti-inflammatory properties.
- berberine rich herbs are effective in lowering blood sugar levels, clearing inflammation and healing mucous membranes. In oriental medicine the right combinations of berberine herbs, such as gardenia, scute, coptis, and phellodendron, have been used for centuries to cure a broad range of inflammatory disorders.
- Boswellia : the boswellia plant, from which the aromatic resin frankincense is derived, contains powerful anti-inflammatory compounds known as boswellic acids.
- Spirulina helps modulate a number of transcription factors linked to causing inflammation, effectively exerting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity when consumed.
- Celery is believed to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may help with ailments attributed to inflammation such as arthritis.
- Grape seed extract contains polyphenols which have been shown in clinical studies to exhibit anti-inflammatory activity
- True Unicorn root contains Diosgenin, an anti-inflammatory.
What to Avoid in the Inflammation Diet
- Omega-6 fatty acids
- Hydrogenated and trans fats found in margarine.
- Processed, packaged, or prepared foods
- Fried foods
- Wheat products
- refined grains (such as those found in white bread and many processed foods): Contain gluten.
- stress
- smoking
- alcohol
- meat
- nightshade plants
- sugary foods (especially containing white, refined sugar)
- Synthetic sweeteners (Nutrasweet, Splenda, saccharin, aspartame, AminoSweet, etc.)
- diary products
- Salt : Choose unrefined salt which naturally contains many different minerals, not just sodium.
- Food additives: colors, flavor enhancers, stabilizers, preservatives, etc.