Diverticulitis
Symptoms
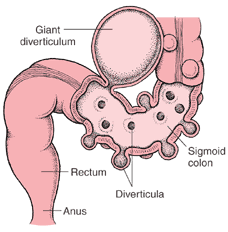
Inflammation of the diverticula (small outpouchings) along the wall of the colon, the large intestine.
For diverticulitis to occur, there must be diverticulosis, the presence of diverticula. Diverticulosis can occur anywhere in the colon but it is most typical in the sigmoid colon, the S-shaped segment of the colon the left lower part of the abdomen..
A key factor promoting the formation of diverticulosis is elevated pressure within the colon. The pressure within the colon is raised when a person is constipated and has to push down to pass small, hard bits of stool ("rabbit droppings").
Most patients with diverticulosis have few or no symptoms although some have mild symptoms including abdominal cramping and bloating.
Diverticulosis sets the stage for inflammation and infection of the outpouching, that is for diverticulitis. (The "-itis" refers to inflammation.) It is potentially serious and can result in pain in the left lower abdomen, fever, nausea, vomiting, constipation and, paradoxically, diarrhea and frequent urination. Even graver consequences such as perforation of the colon and peritonitis are well known from diverticulitis. The incidence of diverticulosis increases with age. Age causes a weakening of the walls of the colon and this weakening permits the formation of diverticula. By age 80, most people have diverticulosis.
Home remedies
- Probiotics : A daily dose of probiotics including Lactobacillus Casei helps keep the intestines healthy, controlling diverticulitis and reducing symptoms of the disease, reports the University of Maryland Medical Center.
- The best way to avoid developing diverticulosis in the first place is by eating a proper healthy diet with plenty of fiber. A diet high in fiber keeps the bowels moving, keeps the pressure within the colon within normal limits, and slows or stops the formation of diverticula.
- liquid diet (fastening) until all painful symptoms have subsided.
Warnings
References
Medical Disclaimer
This information is not meant to be substituted for medical advice. Always consult a medical professional regarding any medical problems and before undertaking any treatment or dietary changes.