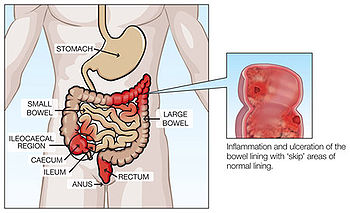
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease, also known as Crohn syndrome and regional enteritis, is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus.
See also :
Causes
A recent study at the Center for Medical Mycology at Case Western Reserve and University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center revealed that three specific bacterial and fungal species were highly correlated with Crohn’s disease—E. coli bacteria, Serratia marcescens bacteria and the fungus Candida tropicalis. Research had previously identified E. coli as a culprit, but this is the first study to show the other two microbes are also highly common in the guts of people with this painful condition.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, and weight loss.[1][2] Other complications may occur outside the gastrointestinal tract and include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and tiredness. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction also commonly occurs and those with the disease are at greater risk of bowel cancer.
Home remedies
- Probiotics : Healthy intestinal flora bestows resistance to intestinal disorders such as constipation, diarrhea, diverticulitis, irritable bowel disease, ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn's Disease, leaky gut syndrome, autoimmunity, and colon cancer.
- Lactobacillus Casei may offer protection in the intestines of people with Crohn's disease.
- Great anti-inflammatory foods include coconut products, berries, and non-denatured, whey protein from grass-fed cows and goats. This protein source is also loaded with L-glutamine and enhances cellular glutathione stores which are both necessary for rebuilding the gut and de-inflaming the body. Anti-inflammatory herbs such as turmeric, ginger, boswellia, cinnamon, rosemary, & oregano among others should be used as much as possible.
- Glutamine has been shown to be effective in people with ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and irritable bowel syndrome.
- Boswellia has been studied for use in Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and collagenous colitis.
- Dysbiosis is a common feature in individuals with auto-immune disease. Naturally fermented foods such as red cabbage sauerkraut, kimchi, & coconut kefir are phenomenal foods for restoring healthy gut bacteria. Additionally, a high quality probiotic supplement with 50+ billion microorganisms should be consumed regularly.
- Coconut Macaroon cookes stops the chronic diarrhea associated with Crohn's Disease.
- a traditional Chinese medicinal tea composed of fennel, flax, and fenugreek, is known to help treat coughs and cold, mucus buildup, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and Crohn's Disease.
- Frankincense is used in traditional medicines to treat inflammatory disorders such as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Crohn's disease.
- Chaga mushroom may help treat inflammatory bowel disease (such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease).
- Probiotics can reverse ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other gut inflammations that occur from a lack of sufficient probiotics.
- Glutamine : even serious gastrointestinal and digestive diseases such as Crohn's, IBS and Colitis can see substantial improvement with glutamine supplementation.
- Keep inflammation low in the intestines is vital for Crohn’s sufferers. A great way to help tame inflammation in any area of the body is to engage the power of Nature’s anti-inflammatory—Omega-3 essential fatty acids.
- Caprylic Acid shows promise in the treatment of Crohn's disease.
- Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) Reduce Crohn’s and Irritable Bowel Disease Symptoms Naturally
- Mastic reduces inflammation and improves antioxidant potential in this inflammatory bowel disease. A study published in the February 7, 2007 issue of the "World Journal of Gastroenterology" researched the efficacy of mastic supplements on people with mild to moderately active Crohn's disease, a type of inflammatory bowel disease. These individuals experienced significant decreases in symptoms and inflammatory markers in plasma after taking mastic for four weeks.
- A low FODMAP diet could have its place as a temporary initial treatment.
Warnings
References
Medical Disclaimer
This information is not meant to be substituted for medical advice. Always consult a medical professional regarding any medical problems and before undertaking any treatment or dietary changes.