Difference between revisions of "Prostatitis"
From Wikiwel
(→Symptoms) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Prostatitis.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Prostatitis]] | [[File:Prostatitis.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Prostatitis]] | ||
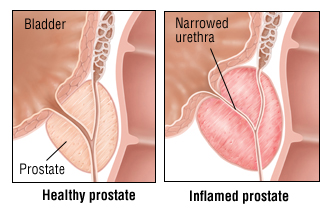
| + | Prostatitis is inflammation or swelling of the prostate gland. When symptoms start gradually and linger for more than a couple of weeks, the condition is called chronic prostatitis. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
* Chronic bacterial prostatitis — In this condition, a bacterial infection causes swelling and inflammation of the prostate. Doctors can definitively make this diagnosis if bacteria and white blood cells are found in the urine. White blood cells are present when there is inflammation that may or may not be related to an actual infection. True chronic bacterial infection accounts for a small percentage of cases of chronic prostatitis. Sometimes doctors suspect a lingering bacterial infection even though no bacteria are identified. | * Chronic bacterial prostatitis — In this condition, a bacterial infection causes swelling and inflammation of the prostate. Doctors can definitively make this diagnosis if bacteria and white blood cells are found in the urine. White blood cells are present when there is inflammation that may or may not be related to an actual infection. True chronic bacterial infection accounts for a small percentage of cases of chronic prostatitis. Sometimes doctors suspect a lingering bacterial infection even though no bacteria are identified. | ||
Revision as of 11:07, 29 September 2013
Prostatitis is inflammation or swelling of the prostate gland. When symptoms start gradually and linger for more than a couple of weeks, the condition is called chronic prostatitis.
Symptoms
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis — In this condition, a bacterial infection causes swelling and inflammation of the prostate. Doctors can definitively make this diagnosis if bacteria and white blood cells are found in the urine. White blood cells are present when there is inflammation that may or may not be related to an actual infection. True chronic bacterial infection accounts for a small percentage of cases of chronic prostatitis. Sometimes doctors suspect a lingering bacterial infection even though no bacteria are identified.
- Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, also called inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome — Doctors make this diagnosis when patients have typical symptoms of chronic prostatitis, but no bacteria are found in a urine sample. The cause of most cases of non-bacterial prostatitis is not well understood. The urine often contains white blood cells. Some patients may have a persistent low-grade infection that cannot be detected in a routine urine sample. However, most patients with non-bacterial prostatitis have no evidence of infection, even when sophisticated tests are done.
- Prostadynia, also called non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome — This term is used when symptoms of prostatitis are present, but there is no evidence of prostate infection or inflammation. Doctors understand very little about why some people — often young, otherwise healthy men — develop this problem. Theories to explain prostadynia include an abnormal buildup of pressure in the urinary tract, irritation resulting from an autoimmune or chemical process, or pain generated in the nerves and muscles within the pelvis.
Home remedies
- Small Flowered Willow Herb extract quickly helps men to recover from the annoying symptoms of prostatitis.
- Pygeum acts as a natural antibiotic. That means it can help relieve symptoms of prostatitis. Prostatitis causes painful urination, back and groin pain, fever and frequent urges to pee.
Warnings
References
Medical Disclaimer
This information is not meant to be substituted for medical advice. Always consult a medical professional regarding any medical problems and before undertaking any treatment or dietary changes.