Tannins
Tannins are polyphenols found principally in the bark, leaves and immature fruit of a wide range of plants. They form complexes with proteins and other plant polymers such as polysaccharides. It is thought that the role of tannins in nature is one of plant defence: they have an astringent, aversive taste that is off-putting to wannabe herbivores. As an animal or insect begins to munch on plant tissue, the tannins are released from cellular compartments and bind with the proteins and other cell components, making them taste unpleasant and rather indigestible.
Contents
Special Precautions of Tannins
- Tannins' numerous hydroxyl radicals confer them a strong avidity for metals such as Fe, Zn and Cu. This property makes them strong inhibitors for the gastrointestinal absorption of these metalsTannins can also impede the body’s ability to absorb iron which may adversely affect an otherwise balanced diet. If, for instance, you are in the habit of drinking coffee or tea while having your meal, the tannins in your drink can retard your body’s absorption of iron from the vegetables in your meal. There is a way though to counter the effect, or at least lessen it, through lemon or milk added to your brewed beverage. Another suggestion is to drink coffee or tea between meals – not during mealtime itself.
- Don't confuse with tannic acid : The main cause of confusion concerning tannins is that they're often mistakenly believed to be associated with tannic acid which is used for tanning leather, when this is not the case. Tannic acid is often extracted from oak leaves and has a completely different chemical makeup than polyphenols, so despite the fact that you may have heard that tea tannins (polyphenols) can be used for tanning leather, this simply is not true.
- Tannins can discolor teeth. This is one reason why dental specialists advise on limiting coffee and tea intake.
- Tannins are also believed to cause migraines in some people, although some medical experts strongly disagree with this, contending that the evidence from relevant researches is inconclusive.
The benefits of Tannins are
Because of their astringency, tannins have been used as the bases of traditional herbal medications. Some of the herbs that are known to contain tannins and are used in the treatment of ailments include sage (to treat sore throats and bleeding gums), blackberry (to halt bleeding from cuts or scrapes), and raspberry (to ease morning sickness in expectant mothers). Most of the other berry varieties are also used to treat diarrhea.
- Tannins are used medicinally as anti-diarrhea and anti-hemorrhoid compounds. Tannins also display anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for gastritis and bowel irritation, as well as moderate antimicrobial effects.
- preventing tooth decay : Most noticeable among tannins’ many characteristics is their being astringent. This styptic power binds proteins located on the surface of the mouth, thereby making the harmful bacteria in the mouth ineffective while putting in check the buildup of plaque and preventing tooth decay.
- Tannins are likewise known to have antioxidant properties which can help prevent cellular damage and, therefore, may protect against heart disease and cancer. In fact, several studies have proven that the polyphenols found in red wine (resveratrol) and in black and green tea (catechins) are antioxidants that carry potential health benefits.
- Treatment or prevention of cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia or obesity : Punicalin, punicalagin, pedunculagin, tellimagrandin, corilagin, granatine a and b, terminalin (Treatment or prevention of cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia or obesity.(US20190000867A1)
- Antioxidant capacity for preventing or treating hypercholesterolemia and/or hypertension : Punicalagins (EP2033526A1)
- Antioxidant or anti-microbial additive, or agent for reducing nitrosamines or mycotoxins : Chestnut tannins (EP2904910B1)
- Treatment of bacterial infections : Ellagitannins (US20110105421A1)
- Inhibition or prevention of obesity, lipid storage (reducing blood triglyceride levels), hyperlipemia, arteriosclerosis and thrombosis : GA, EA, isoquercitrin, tellimagrandin I and II, pedunculagin, TGGs, PGG and di-galloyl-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-D-glucose (US7687085B2)
- Regulation of the synthesis and secretion of cytokines, including TNF-alpha and IL-1-Beta : Gallotannins and ellagitannins(US20080070850A1)
- Anti-inflammatory or anti-allergic agent by the inhibition of histamine release from mast cells. Regular oral administration of product can ameliorate or prevent rhinitis, atopic dermatitis or asthmaEllagitannins (EP0727218A3)
- Inhibition of the propagation in human cells of a human retrovirus (HIV) : 1,3,4-tri-galloylquinic acid, galloylshikimic acid derivatives strictinin, corilagin, castalagin, vescalagin, chebulinic acid, chebulagic acid, punicalin, punicalagin, punicacortein C, cannamtannin B2 (CA2001898A1)
- Inhibition of Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) growth, anti-inflammation and leukemia treatment : Tellimagrandin (US8975234B2)
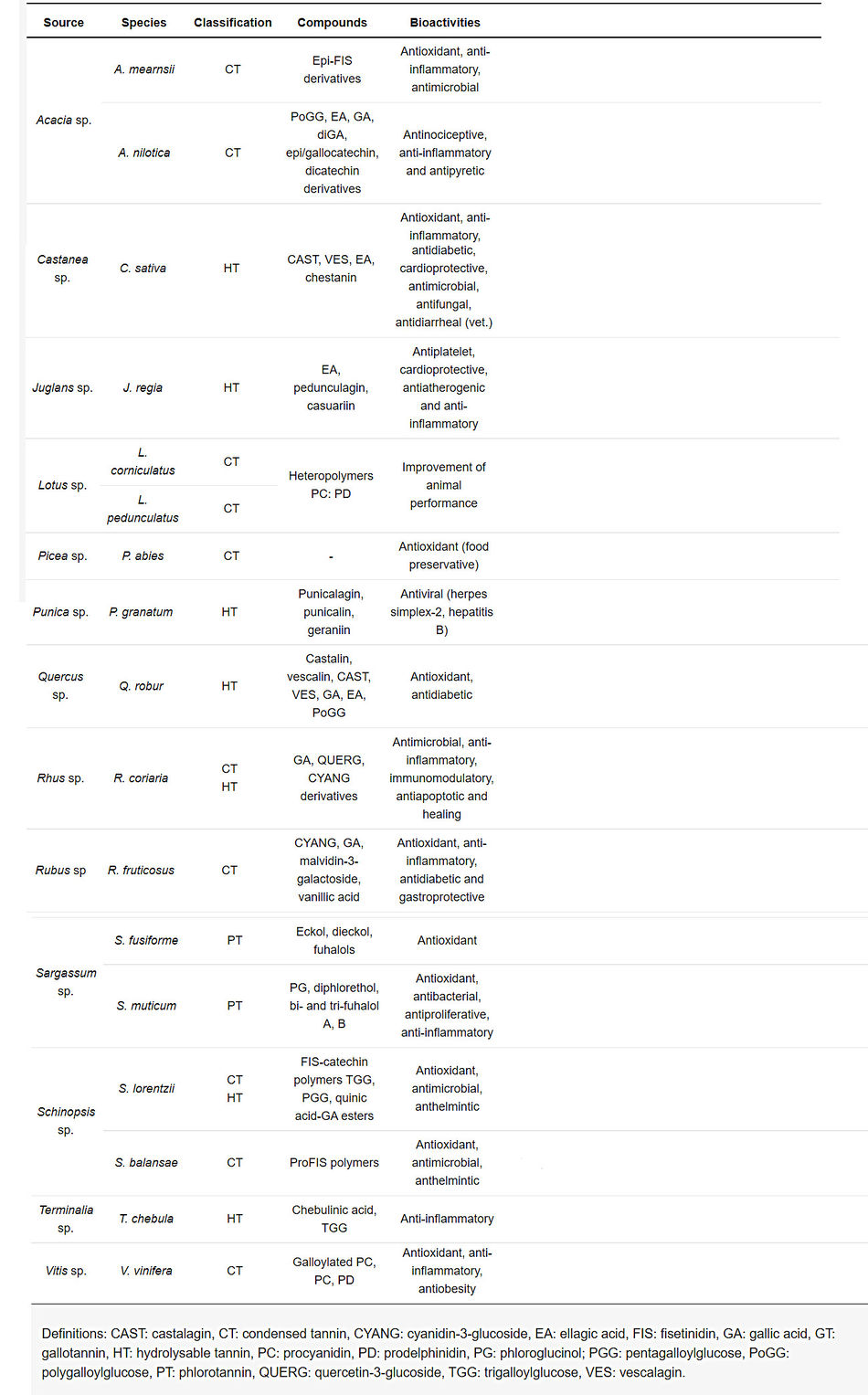
Table : Tannin-rich genera with some representatives and their tannin chemical profile, including major compounds and their reported bioactivities.
References
By-Products of Agri-Food Industry as Tannin-Rich Sources: A Review of Tannins' Biological Activities and Their Potential for Valorization, María Fraga-Corral, Paz Otero, Javier Echave, Paula Garcia-Oliveira, Maria Carpena, Amira Jarboui, Bernabé Nuñez-Estevez, Jesus Simal-Gandara and Miguel A. Prieto