Vitamin E
Other Names: Acétate d’Alpha Tocophérol, Acétate d’Alpha Tocophéryl, Acétate de D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Acétate de DL-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Acétate de Tocophérol, Acétate de Tocophéryl, Acétate de Vitamine E, All Rac-Alpha-Tocopherol, All-Rac-Alpha-Tocophérol, Alpha-Tocophérol, Alpha Tocopherol Acetate, Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate, Alpha tocotrienol, Alpha tocotriénol, Alpha-tocopherol, Alpha-Tocophérol, Beta tocotrienol, Bêta-tocotriénol, Beta-tocopherol, Bêta-tocophérol, Concentré de Tocotriénol, D-Alpha Tocopherol, D-Alpha Tocophérol, D-Alpha Tocopheryl Succinate, D-Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate, D-Alpha Tocotrienol, D-Alpha Tocotriénol, D-Alpha-Tocopherol, D-Alpha-Tocophérol, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acid Succinate, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Succinate, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl, D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, D-Beta-Tocopherol, D-Bêta-Tocophérol, D-Delta-Tocopherol, D-Delta-Tocophérol, Delta Tocotrienol, Delta-Tocotriénol, Delta-tocopherol, Delta-tocophérol, D-Gamma Tocotrienol, D-Gamma-Tocotriénol, D-Gamma-Tocopherol, D-Gamma-Tocophérol, DL-Alpha-Tocopherol, DL-Alpha-Tocophérol, DL-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate, DL-Alpha-Tocopheryl, DL-Alpha-Tocophéryl, DL-Tocopherol, DL-Tocophérol, D-Tocopherol, D-Tocophérol, D-Tocopheryl Acetate, Fat-Soluble Vitamin, Gamma tocotrienol, Gamma-tocotriénol, Gamma-tocopherol, Gamma-tocophérol, Mixed Tocopherols, Mixed Tocotrienols, Palm Tocotrienols, Rice Tocotrienols, RRR-Alpha-Tocopherol, RRR-Alpha-Tocophérol, Succinate Acide de D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Succinate Acide de Tocophéryl, Succinate de D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Succinate de Tocophéryl, Succinate de Vitamine E, Tocopherol Acetate, Tocopherol, Tocophérol, Tocophérols Mixtes, Tocotriénols de Palme, Tocotriénols de Riz, Tocotriénols Mixtes, Tocopheryl Acetate, Tocopheryl Acid Succinate, Tocopheryl Succinate, Tocotrienol, Tocotriénol, Tocotrienol Concentrate, Tocotrienols, Tocotriénols, Vitamin E Acetate, Vitamin E Succinate, Vitamina E, Vitamine E, Vitamine Liposoluble, Vitamine Soluble dans les Graisses.
- Vitamin E is a member of the fat-soluble family of vitamins that also includes vitamin D, vitamin K and vitamin A. Vitamin E is important as an antioxidant that protects the cells of your body from free radical damage. Vitamin E is also an important component of the immune system and is necessary to repair DNA.
- Vitamin E is found in nuts, seeds, vegetables oils, cereals and dark green leafy vegetables. Vitamin E deficiency is rare. Vitamin E supplements have been recommended for the prevention of heart disease and some forms of cancer. Research studies have given mixed results, so there is not enough evidence to back up these claims. Vitamin E, along with other antioxidants and zinc has been used successfully to reduce the risk of advanced macular degeneration.
Special Precautions of Vitamin E
- Recent studies conclude that SYNTHETIC dl-alpha-tocopheryl-acetate Vitamin E supplements may have an increased risk of prostate cancer in healthy men even after they stopped taking them.
- Vitamin E is LIKELY SAFE for most healthy people when taken by mouth or applied to the skin. Most people do not experience any side effects when taking the recommended daily dose, which is 15 mg.
- Vitamin E is POSSIBLY UNSAFE if taken in high doses. If you have a condition such as heart disease or diabetes, don’t take doses of 400 IU/day or more. Some research suggests that high doses might increase the chance of death and possibly cause other serious side effects. The higher the dose, the greater the risk of serious side effects.
- There is some concern that vitamin E might increase the chance of having a serious stroke called hemorrhagic stroke, which is bleeding into the brain. Some research shows that taking vitamin E in doses of 300-800 IU each day might increase the chance of this kind of stroke by 22%. However, in contrast, vitamin E might decrease the chance of having a less severe stroke called an ischemic stroke.
- There is contradictory information about the effect of vitamin E on the chance of developing prostate cancer. Some research suggests that taking large amounts of a multivitamin plus a separate vitamin E supplement might actually increase the chance of developing prostate cancer in some men.
- High doses can also cause nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps, fatigue, weakness, headache, blurred vision, rash, and bruising and bleeding.
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: When used in the recommended daily amount, vitamin E is POSSIBLY SAFE for pregnant and breast-feeding women. There has been some concern that taking vitamin E supplements might be harmful to the fetus when taken in early pregnancy. But it is too soon to know if this is an important concern. Until more is known, do no take vitamin E supplements during early pregnancy without talking with your healthcare provider.
- Angioplasty, a heart procedure: Avoid taking supplements containing vitamin E or other antioxidant vitamins (beta-carotene, vitamin C) immediately before and following angioplasty without the supervision of a health care professional. These vitamins seem to interfere with proper healing.
- Low levels of vitamin K (vitamin K deficiency): Vitamin E might worsen clotting problems in people whose levels of vitamin K are too low.
- An eye condition called retinitis pigmentosa: All-rac-alpha-tocopherol (synthetic vitamin E) 400 IU seems to speed vision loss in people with retinitis pigmentosa. However, much lower amounts (3 IU) don’t seem to produce this effect. If you have this condition, it’s best to avoid vitamin E.
- Bleeding disorders: Vitamin E might make bleeding disorders worse. If you have a bleeding disorder, avoid taking vitamin E supplements.
- Prostate cancer: There is concern that taking vitamin E might increase the chance of developing prostate cancer. The effect of vitamin E in men who currently have prostate cancer is not clear. But, in theory, taking vitamin E supplements might worsen prostate cancer in men who already have it.
- Head and neck cancer: Don’t take vitamin E supplements in doses of 400 IU/day or more. Vitamin E might increase the chance that cancer will return.
- Surgery: Vitamin E might increase the risk of bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using vitamin E at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
- Cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune) interacts with VITAMIN E : Taking large amounts of vitamin E along with cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune) might increase how much cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune) the body absorbs. By increasing how much cyclosporine the body absorbs, vitamin E might increase the effects and side effects of cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune).
- Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) substrates) interacts with VITAMIN E. Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Vitamin E might increase how quickly the liver breaks down some medications. Taking vitamin E along with some medications that are broken down by the liver can decrease the effectiveness of some medications. Before taking vitamin E talk to your healthcare provider if you are taking any medications that are changed by the liver.Some medications changed by the liver include lovastatin (Mevacor), ketoconazole (Nizoral), itraconazole (Sporanox), fexofenadine (Allegra), triazolam (Halcion), and many others.
- Medications for cancer (Chemotherapy) interacts with VITAMIN E. Vitamin E is an antioxidant. There is some concern that antioxidants might decrease the effectiveness of some medications used for cancers. But it is too soon to know if the interaction occurs.
- Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs) interacts with VITAMIN E
- Vitamin E might slow blood clotting. Taking vitamin E along with medications that also slow clotting might increase the chances of bruising and bleeding.Some medications that slow blood clotting include aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), diclofenac (Voltaren, Cataflam, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others), naproxen (Anaprox, Naprosyn, others), dalteparin (Fragmin), enoxaparin (Lovenox), heparin, warfarin (Coumadin), and others.
- Medications used for lowering cholesterol (Statins) interacts with VITAMIN E. Taking vitamin E, beta-carotene, vitamin C, and selenium together might decrease the effectiveness of some medications used for lowering cholesterol. It is not known if taking vitamin E alone decreases the effectiveness of some medications used for lowering cholesterol.Some medications used for lowering cholesterol include atorvastatin (Lipitor), fluvastatin (Lescol), lovastatin (Mevacor), and pravastatin (Pravachol).
- Niacin interacts with VITAMIN E
- Taking vitamin E along with beta-carotene, vitamin C, and selenium might decrease some of the beneficial effects of niacin. Niacin can increase the good cholesterol. Taking vitamin E along with these other vitamins might decrease the good cholesterol.
- Warfarin (Coumadin) interacts with VITAMIN E
- Warfarin (Coumadin) is used to slow blood clotting. Vitamin E can also slow blood clotting. Taking vitamin E along with warfarin (Coumadin) can increase the chances of bruising and bleeding. Be sure to have your blood checked regularly. The dose of your warfarin (Coumadin) might need to be changed
The benefits of Vitamin E are
- Bladder cancer. Taking 200 IU of vitamin E by mouth for more than 10 years seems to help prevent death from bladder cancer.
- Alzheimer’s disease. Vitamin E might slow down the worsening of memory loss in people with moderately severe Alzheimer’s disease. But vitamin E does not seem to prevent moving from mild memory problems to full-blown Alzheimer’s disease.
- Painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea). Taking vitamin E for 2 days before and for 3 days after bleeding begins seems to decrease pain severity and duration, and reduce menstrual blood loss.
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Taking vitamin E by mouth seems to reduce anxiety, craving, and depression in some women with PMS.
- Chemotherapy-related nerve damage. Taking vitamin E before and after treatment with cisplatin chemotherapy might reduce the chance of getting nerve damage.
- Ischemic stroke. Some research shows that taking vitamin E might slightly decrease the chance of having a stroke caused by a blood clot (ischemic stroke). But taking vitamin E might also increase the chance of having a more severe type of stroke, called hemorrhagic stroke. This kind of stroke occurs when there is bleeding into the brain.
- Liver disease called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Taking vitamin E 400-1200 IU daily seems to significantly improve symptoms in adults and children after 4-24 months of treatment.
- Huntington’s chorea. Natural vitamin E (RRR-alpha-tocopherol) can significantly improve symptoms in people with early Huntington’s disease, but it doesn’t seem to help people with more advanced disease.
- Macular degeneration. Taking vitamin E by mouth in combination with vitamin C, beta-carotene and zinc might slow the worsening of advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD). There isn’t enough information to know if this combination helps people with less advanced macular disease or prevents AMD. Zinc needs to be present in the combination for there to be any effect on AMD.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Vitamin E taken along with standard treatment is better than standard treatment alone for reducing pain in people with RA. But this combination doesn’t reduce swelling (inflammation).
- Male infertility.
- High blood pressure during pregnancy (pre-eclampsia).
- Movement disorders called tardive dyskinesia and dyspraxia.
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Kidney problems in children (glomerulosclerosis).
- Helping to treat an inherited disorder called G6PD deficiency.
- Beta-thalassemia.
- Dementia.
- Healing a type of skin sore called granuloma annulare when put on the skin.
- Uveitis.
- Sunburn.
- Helping the eyes heal after surgery.
- Treating a type of eye disease in newborns called retrolental fibroplasia.
- Decreasing brain and heart bleeding in premature babies.
- Helping some heart medications called “nitrates” work better.
- Improving physical performance and strength in the elderly.
- Fibrosis caused by radiation.
- Mercury Detox : A combination of vitamin E and Selenium products may help reduce the toxicity of mercury from eating fish.
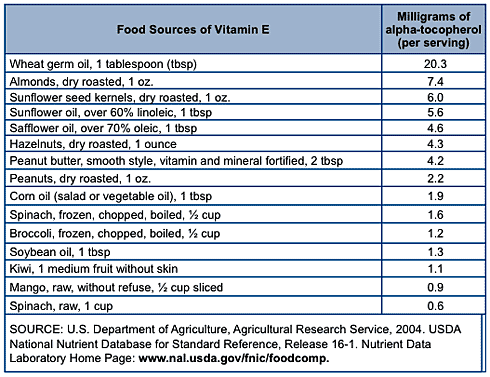
Food Sources
Vitamin E is present in a wide range of whole foods."Good sources of vitamin E include vegetable oils, sweet potatoes, avocados, nuts, sunflower seeds and soybeans. Smaller amounts are found in egg yolks and green leafy vegetables. Alpha-tocopherol is more abundant in sunflower and wheat germ oils, whereas corn and soybean oils have higher levels of gamma-tocopherol.
- Red Clover contains Vitamin E in the form of Tocopherol which is a very potent antioxidant known to help fight cancer as well as Heart Disease.
- two forms of vitamin E, gamma and delta-tocopherols found in soybean, canola and corn oils as well as nuts prevent colon, lung, breast and prostate cancers.