Category:Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine is an ancient practice still used by millions of people all over the world -- even after the development of modern scientific medicine. At the root of traditional Chinese medicine is the belief that the individual (microcosm) is viewed as an integral part of the forces of nature (macrocosm). By careful observation of nature, Taoist sages were able to perceive patterns common to both the external environment and the internal climate of the human body. Over a period of thousands of years, the cumulative observations of sages all over China led to an intricate system of diagnosis and healing. The basic principles are rather distinctive:
- Relative Properties - Yin and Yang : The Physiology of Chinese medicine holds that the human body's life is the result of the balance of yin and yang. Yin is the inner and negative principles, and yang, outer and positive. The key reason why there is sickness is because the two aspects lose their harmony. Seen from the recovery mechanism of organs, yang functions to protect from outer harm, and yin is the inner base to store and provide energy for its counterpart.
- Basic Substance : Doctors of traditional Chinese medicine (abbreviated to TCM) believe that vital energy - moving and energetic particles, state of blood, and body fluid are the essential substances that compose together to form the human body, and the basis for internal organs to process. They are channeled along a network within the body - Jing Luo as their channels. On the physical side, vital energy serving to promote and warm belongs to the properties of yang, and blood and body fluid to moisten possesses the properties of yin.
Five Phases theory
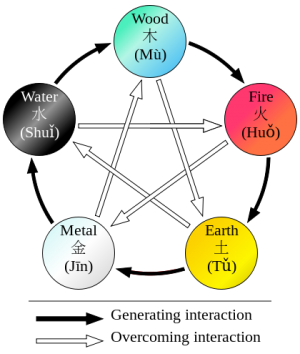
Five Phases (五行), sometimes also translated as the "Five Elements" theory, presumes that all phenomena of the universe and nature can be broken down into five elemental qualities – represented by wood (木), fire (火), earth (土), metal (金), and water (水).In this way, lines of correspondence can be drawn:
| Phenomenon | Wood | Fire | Earth | Metal | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | east | south | center | west | north |
| Colour | green/blue | red | yellow | white | black |
| Climate | wind | heat | damp | dryness | cold |
| Taste | sour | bitter | sweet | acrid | salty |
| Zang Organ | Liver | Heart | Spleen | Lung | Kidney |
| Fu Organ | Gallbladder | Small Intestine | Stomach | Large Intestine | Bladder |
| Sense organ | eye | tongue | mouth | nose | ears |
| Facial part | above bridge of nose | between eyes, lower part | bridge of nose | between eyes, middle part | cheeks (below cheekbone) |
| Eye part | iris | inner/outer corner of the eye | upper and lower lid | sclera | pupil |
Strict rules are identified to apply to the relationships between the Five Phases in terms of sequence, of acting on each other, of counteraction etc. All these aspects of Five Phases theory constitute the basis of the Zàng-fǔ concept, and thus have great influence regarding the TCM model of the body.
Correspondences between the body and the universe have historically not only been seen in terms of the Five Elements, but also of the "Great Numbers" (大數)For example, the number of acu-points has at times been seen to be 365, in correspondence with the number of days in a year; and the number of main meridians – 12 – has been seen in correspondence with the number of rivers flowing through the History of China|ancient Chinese empire.
Diagnosis
Four Methods of Diagnosis : It is a wonder that TCM doctors could cure countless patients without any assistant apparatus but only a physical examination. The four methods of diagnosis consist of observation, auscultation and olfaction, interrogation, pulse taking and palpation.
- Observation indicates that doctors directly watch the outward appearance to know a patient's condition. As the exterior and interior corresponds immediately, when the inner organs run wrongly, it will be reflected through skin pallor, tongue, the facial sensory organs and some excrement.
- Auscultation and olfaction is a way for doctors to collect messages through hearing the sound and smelling the odor. This is another reference for diagnosis.
- Interrogation suggests that doctors question the patient and his relatives, so as to know the symptoms, evolution of the disease and previous treatments.
- The taking of the pulse and palpation refer that doctors noting the pulse condition of patients on the radial artery, and then to know the inner change of symptom. Doctors believe that when the organic function is normal, the pulse, frequency, and intension of pulse will be relatively stable, and when not, variant.
When treating a disease, doctors of TCM usually find the patient's condition through these four diagnostic methods: observation, auscultation and olfaction, interrogation, pulse, and palpation. Combining the collected facts and according to their internal relations, doctors will utilize the dialectics to analyze the source and virtue of the disease. Then make sure what prescription should be given. In traditional Chinese medical science, the drugs are also different from the West, because doctors have discovered the medicinal effects of thousand of herbs over a long period of time. Before taking the medicine, the patient will have to boil it. Then there is the distinctive method of preparation, associated with the acupuncture and massage, the treatment will take effect magically.
Such a complicated medical science had come down thanks to records like The Yellow Emperor's Canon of Interior Medicine, Shen Nong's Canon of Herbs, and the Compendium of Materia Medica, which are all comprehensive and profound works. There are also wide-spread stories praising the experienced and notable doctors in ancient China like Hua Tuo in the Three Kingdoms Periods (220 - 280). Today, though western medicine has been adopted, traditional treatments are still playing an important role and have raised great attention and interest worldwide due to the amazing curative effects reported.
Pages in category "Chinese medicine"
The following 200 pages are in this category, out of 419 total.
(previous 200) (next 200)